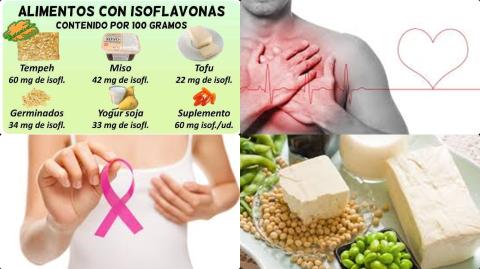
Objectives:
Do dietary intakes of soy, soy isoflavones and soy protein reduce risk of mortality from all causes, cancers and cardiovascular diseases?
Study design:
This review article included 23 prospective cohort studies with an overall sample size of 330,826 participants.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found soy/soy products consumption significantly reduced risk of mortality from cancers with 12% [pooled relative risk = 0.88, 95% CI = 0.79 to 0.99, p = 0.03, I2 = 47.1%].
The investigators found soy/soy products consumption significantly reduced risk of mortality from cardiovascular diseases with 15% [pooled effect size = 0.85, 95% CI = 0.72 to 0.99, p = 0.04, I2 = 50.0%].
The investigators found such significant associations were also observed for all-cause mortality in some subgroups of the included studies, particularly those with higher quality.
The investigators found in addition, higher dietary intake of soy was associated with decreased risk of mortality from gastric, colorectal and lung cancers as well as ischemic cardiovascular diseases.
The investigators found participants in the highest category of dietary soy isoflavones intake had a 10% lower risk of all-cause mortality compared with those in the lowest category.
The investigators found that a 10-mg/day increase in dietary intake of soy isoflavones was associated with 7% and 9% decreased risk of mortality from all cancers and breast cancer, respectively.
The investigators found for each 5-g/day increase in consumption of soy protein a 12% reduction in breast cancer death.
The investigators found, however, dietary intake of soy protein was not significantly associated with all-cause and cardiovascular diseases mortality.
The investigators concluded that soy and its isoflavones consumption favorably influence risk of mortality. In addition, soy protein dietary intake is associated with a decreased risk in the mortality of breast cancer. These findings support the current recommendations to increase intake of soy for greater longevity.
Original title:
Soy, Soy Isoflavones, and Protein Intake in Relation to Mortality from All Causes, Cancers, and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies by Nachvak SM, Moradi S, […], Sadeghi O.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31278047
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on soy consumption, cardiovascular diseases and breast cancer right here.