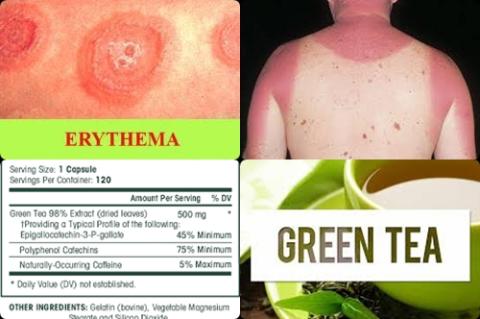
540 mg/d green tea catechins supplementation reduces UV-induced damage due to erythema inflammation
Objectives:
Catechins are a part of the chemical family of flavonoids, a naturally occurring antioxidant, and a secondary metabolite in certain plants. Green tea catechins are well recognized for their essential anti-inflammatory, photo-protective, antioxidant and chemo-preventive functions. Ultraviolet radiation is a principal cause of damage to the skin. Studies observed that regular intake of green tea catechins increased the minimal dose of radiation required to induce erythema. However, there is a gap in knowledge regarding the impact of oral supplementation with green tea catechins on ultraviolet radiation-induced skin inflammation in human subjects. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Is green tea catechin supplementation associated with protection against UV-induced damage due to erythema inflammation in humans?
Study design:
This review article included 6 randomized controlled studies with a total of 100 healthy volunteers. The intervention duration of administrated green tea catechins orally varied from 6 to 12 weeks.
All studies included in this systematic review and meta-analysis measured the erythema index using solar simulator techniques, wherein the blue-light (mimicking sunlight) solar simulator was used to irradiate the skin and skin color was evaluated by chromameter before and 24 h after irradiation at baseline and post-supplementation of green tea catechins.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found meta-analysis results confirmed oral supplementation of green tea catechins was highly effective at low-intensity ultraviolet radiation-induced erythema response [MED range = 1.25 to 1.30] compared to placebo, showing a significant pooling difference in erythema index [SMD = -0.35, 95% CI = -0.57 to -0.13, p = 0.002, I2 = 4%, p = 0.40] in the random-effects model.
The investigators concluded that regular green tea catechin supplementation (as low as 540 mg of green tea catechins per day) is associated with protection against UV-induced damage due to erythema inflammation in humans, wherein green tea catechin metabolites are bioavailable at the dermis and epidermis levels of the skin and thus increase the minimal dose of radiation (MED) required to induce erythema. This in turn suggests that green tea catechins can strengthen the skin’s tolerance to ultraviolet radiation-induced skin damage from radiation through the prevention of the ultraviolet radiation-induced perturbation of epidermal barrier functions.
Original title:
Green Tea Catechin Association with Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Erythema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis by Kapoor MP, Sugita M, [...], Okubo T.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8233826/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about review article/significant and green tea.
Sunburn, also called UV-induced or solar erythema, is characterized by painful blistering and sometimes second degree burn.