A low GI diet decreases LDL-cholesterol
Objectives:
Low glycaemic index (GI) diets are beneficial in the management of hyperglycemia. Cardiovascular diseases are the major cause of mortality in diabetes therefore it is important to understand the effects of GI on blood lipids. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does a low GI diet lower the cholesterol levels?
Study design:
This review article included 28 RCTs comparing low with high GI diets over at least 4 weeks. These 28 RCTs contained 1272 participants with studies ranged from 6 to 155 participants, one was powered on blood lipids and 3 had adequate allocation concealment.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found that compared to high GI diet low GI diet significantly reduced total cholesterol by 0.13 mmol/L [95% CI = -0.22 to -0.04, p = 0.004, 27 trials, 1441 participants]. Significantly means, it can be said with 95% confidence that low GI diet really lowered the total cholesterol levels with 0.13 mmol/L.
The investigators found that compared to high GI diet low GI diet significantly reduced LDL-cholesterol by 0.16 mmol/L [95% CI = -0.24 to -0.08, p 0.0001, 23 studies, 1281 participants]. Significantly, because the p-value was less than 0.05.
The investigators found subgroup analyses suggested that reductions in LDL-cholesterol were greatest in studies of shortest duration and greatest magnitude of GI reduction. Furthermore, lipid improvements appeared greatest and most reliable when the low GI intervention was accompanied by an increase in dietary fiber.
The investigators found sensitivity analyses, removing studies without adequate allocation concealment, lost statistical significance but retained suggested mean falls of 0.10 mmol/L in both.
The investigators found no effects on HDL-cholesterol [MD = -0.03 mmol/L, 95% CI = -0.06 to 0.00, I2 = 0%], or triglycerides [MD was 0.01 mmol/L, 95% CI = -0.06 to 0.08, I2 = 0%].
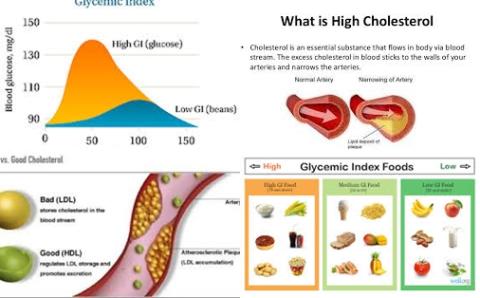
The researchers concluded that low GI diets reduce total and LDL-cholesterol (bad cholesterol) but had no effect on HDL-cholesterol (good cholesterol) or triglycerides.
Original title:
Low glycemic index diets and blood lipids: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials by Goff LM, Cowland DE, [...], Frost GS.
Link:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0939475312001524
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on cholesterol and cardiovascular disease right here.
High LDL-cholesterol levels and high triglyceride levels increase the risk of getting cardiovascular diseases whereas high HDL-cholesterol levels decrease the risk of getting cardiovascular diseases.
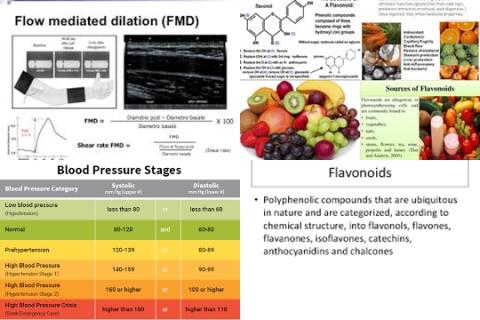
A low GI diet is a diet with a GI value of 55 or lower.