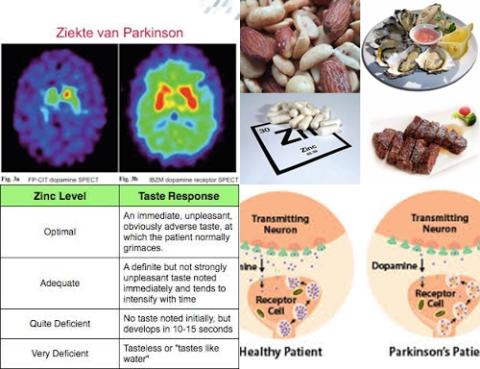
Objectives:
The prevalence of overweight/obesity in adults is raised to 39%, which is nearly tripled more than 1975. The alteration of the gut microbiome has been widely accepted as one of the main causal factors. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does probiotics supplementation prevent overweight/obesity in adults?
Study design:
This review article included 12 RCTs (11 randomized, double-blinded, controlled trials and 1 randomized, single-blinded, controlled trial) with a total of 821 participants (416 participants were given placebo and 405 participants were given probiotics).
7 RCTs included participants who consumed two or multiple strains of probiotics and 5 RCTs included participants who consumed a single strain of probiotics.
7 RCTs investigated a high dosage of probiotics (>1010 CFU) and 5 RCTs investigated lower dosage of probiotics (1010 CFU).
Probiotics were administered in different forms, including sachet, capsule, powder, kefir, yogurt and fermented milk.
Duration of the probiotics supplementation ranged from 8 to 24 weeks.
There was no significant publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation resulted in a significantly reduction in body weight [WMD = -0.55, 95% CI = -0.91 to -0.19 kg, I2 = 64%, p = 0.003].
Subgroup analyses stratified by probiotics dosage, the number of probiotics strains or forms of probiotics showed the effects of probiotics supplementation on body weight were significantly reduced in trials with high dose of probiotics [WMD = -0.58, 95% CI = -0.92 to 0.23 kg], a single strain of probiotics [WMD = -0.49, 95% CI = -0.92 to -0.07 kg] and the capsule or powder of probiotics [WMD = -0.55, 95% CI = -0.84 to -0.26 kg].
Sensitivity analyses revealed that no particular studies significantly affected the summary effects of body weight.
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation resulted in a significantly reduction in BMI [WMD = -0.30, 95% CI = -0.43 to -0.18 kg/m2, I2 = 59%, p = 0.006].
Subgroup analyses stratified by probiotics dosage, the number of probiotics strains or forms of probiotics showed the effects of probiotics supplementation on BMI were significantly reduced with the high dose [WMD = -0.29, 95% CI = -0.46 to -0.12 kg/m2] and single strain of probiotics [WMD = -0.36, 95% CI = -0.52 to -0.20 kg/m2].
Sensitivity analyses revealed that no particular studies significantly affected the summary effects of BMI.
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation resulted in a significantly reduction in waist circumference [WMD = -1.20, 95% CI = -2.21 to -0.19 cm, p = 0.02, I2 = 90%, p 0.00001].
Subgroup analyses stratified by probiotics dosage, the number of probiotics strains or forms of probiotics indicated the effects of probiotics supplementation on waist circumference were significantly reduced in trials with high dose of probiotics [WMD = -1.53, 95% CI = -2.64 to -0.41 cm], a single strain of probiotics [WMD = -1.69, 95% CI = -3.04 to -0.33 cm] and the food form of probiotics [WMD = -1.11, 95% CI = -1.64 to -0.59 cm].
Sensitivity analyses revealed that no particular studies significantly affected the summary effects of waist circumference.
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation resulted in a significantly reduction in fat mass [WMD = -0.91, 95% CI = -1.19 to -0.63 kg, p 0.00001, I2 = 43%, p = 0.08] and fat percentage [WMD = -0.92, 95% CI = -1.27 to -0.56%, p 0.00001, I2 = 57%, p = 0.04].
Subgroup analyses stratified by probiotics dosage, the number of probiotics strains and forms of probiotics indicated that the effect of probiotics supplementation on fat mass was significantly reduced, showing a greater decrease in fat mass with high dosage probiotics WMD -1.08, 95% CI = -1.21 to -0.95 kg] compared to low dosage probiotics [WMD = -1.00, 95% CI = -1.59 to -0.42 kg], a greater decrease with single strain probiotics [WMD = -1.15, 95% CI = -1.28 to -1.02 kg] compared to multiple strain probiotics [WMD = -0.60, 95% CI = -0.94 to -0.26] kg] and a greater decrease with administration probiotics in the form of food [WMD = -1.13, 95% CI = -1.58 to -0.67 kg] compared to in the forms of capsule or powder [WMD = -1.07, 95% CI = -1.20 to -0.94 kg].
No particular study significantly affected the pooled effect of probiotics on fat mass and fat percentage by sensitivity analyses.
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation significantly improved total cholesterol levels [SMD = -0.43, 95% CI = -0.80 to -0.07, p = 0.02, I2 = 73%, p = 0.001].
Subgroup analyses only stratified by probiotics dosage and the number of probiotics strains indicated the effects of probiotics supplementation on total cholesterol were significantly reduced in trials with single strain probiotics [WMD = -0.61, 95% CI = -1.54 to -0.32], compared to multiple strain probiotics [WMD = -0.39, 95% CI = -0.66 to -0.13].
Sensitivity analyses revealed that no particular studies significantly affected the summary effects of total cholesterol.
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation significantly improved LDL-cholesterol levels [SMD = -0.41, 95% CI = -0.77 to -0.04, p = 0.03, I2 = 73%, p = 0.001].
Subgroup analyses stratified by probiotics dosage and the number of probiotics strains indicated the effects of probiotics supplementation on LDL-cholesterol were significantly reduced in trials with multiple strain probiotics [WMD = -0.33, 95% CI = -0.57 to -0.09]. Sensitivity analyses revealed that no particular studies significantly affected the summary effects of LDL-cholesterol.
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation significantly improved fasting plasma glucose (FPG) [SMD = -0.35, 95% CI = -0.67 to -0.02, p = 0.04, I2 = 64%, p = 0.02].
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation significantly improved insulin [SMD = -0.44, 95% CI = -0.84 to -0.03, p = 0.03, I2 = 76%, p = 0.0008].
The investigators found compared with control groups, probiotics supplementation significantly improved HOMA-IR [SMD = -0.51, 95% CI = -0.96 to -0.05, p = 0.03, I2 = 76%, p = 0.003].
The investigators concluded probiotics supplementation during 8 to 24 weeks reduces the body weight and fat mass and improves some of the lipid and glucose metabolism parameters, although some of the effects were small. Probiotics may become a new potential strategy for the prevention and treatment of overweight/obesity in adult individuals.
Original title:
The Potential Role of Probiotics in Controlling Overweight/Obesity and Associated Metabolic Parameters in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis by Wang ZB, Xin SS, [...], Zhang XD.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6500612/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on probiotics, cholesterol, diabetes and obesity/overweight right here.