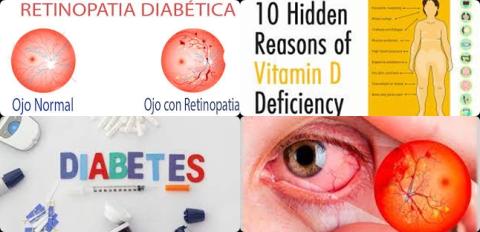
Vitamin D deficiency increases blindness in people with diabetes
Objectives:
Vitamin D levels have been shown to be associated with diabetic retinopathy, however to date, no review has examined the relationship between vitamin D and sight threatening diabetic retinopathy (STDR) and non-sight threatening diabetic retinopathy (NSTDR). Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does vitamin D deficiency (defined as 25(OH)D levels of 20 ng/mL) increase risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with diabetes?
Study design:
This review article included 11 cross-sectional studies and 1 case-control study with a total of 9,057 participants.
There was no publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found vitamin D deficiency significantly increased risk of sight threatening diabetic retinopathy with 80% [OR = 1.80, 95% CI = 1.40 to 2.30, p ≤ 0.001, I2 = 39.39%].
However, this increased risk was not found for non-sight threatening diabetic retinopathy [OR = 1.10, 95% CI = 0.90 to 1.27, p = 0.48, I2 = 30.21%].
The investigators concluded that vitamin D deficiency (defined as 25(OH)D levels of 20 ng/mL) increases risk of sight threatening diabetic retinopathy but not non-sight threatening diabetic retinopathy. Given the well-reported associations between vitamin D deficiency and other unfavourable outcomes, it is important that vitamin D deficiency is managed appropriately and in a timely manner to reduce the risk of blindness in people with diabetes.
Original title:
Associations between vitamin D status and sight threatening and non-sight threatening diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis by Trott M, Driscoll R, […], Pardhan S.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9167360/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on vitamin D and diabetes right here.
Diabetic retinopathy, also known as diabetic eye disease (DED), is a complication of diabetes, caused by high blood sugar levels damaging the back of the eye (retina). It can cause blindness if left undiagnosed and untreated.



