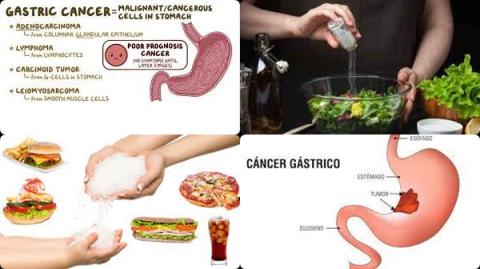
High salt intake increases gastric cancer
Objectives:
Systematic reviews of case-control studies evaluating the relationship between dietary salt intake and gastric cancer showed a positive association, however a quantitative analysis of longitudinal cohort studies is lacking. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does a high salt intake increase gastric cancer risk?
Study design:
This review article contained 10 cohort studies with 268,718 participants, of which 1,474 gastric cancer events and a follow-up of 6-15 years.
Meta-regression analyses did not detect specific sources of heterogeneity.
There was no evidence of publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found for high vs low salt intake a significantly increased risk of 68% for gastric cancer [RR = 1.68, 95% CI = 1.17 to 2.41, p = 0.005].
The investigators found for moderate vs low salt intake a significant increased risk of 41% for gastric cancer [RR = 1.41, 95% CI = 1.03 to 1.93, p = 0.032].
The investigators found the association was stronger in the Japanese population and higher consumption of selected salt-rich foods was also associated with greater risk.
The investigators concluded high salt intake is directly associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer in prospective population studies, with progressively increasing risk across consumption levels.
Original title:
Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies by D’Elia L, Rossi G, […], Strazzullo P.
Link:
http://www.clinicalnutritionjournal.com/article/S0261-5614%2812%2900005-2/abstract
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more studies/information on sodium/salt and cancer right here.
According to WHO, a high salt intake is a salt intake of more than 5 grams salt per day.
A diet with more than 5 grams salt per day is a diet with mainly products/meals with more than 0.25 grams salt per 100 kcal. Check here which products contain maximum 5 grams salt per 100 kcal.
Use the 7-points nutritional profile app to see whether your daily diet contains maximum 5 grams salt per 100 kcal.