Objectives:
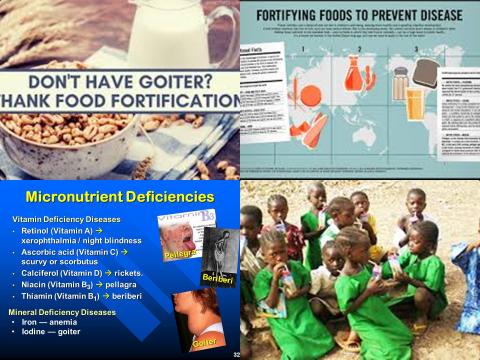
Micronutrient malnutrition is highly prevalent in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and disproportionately affects women and children. Although the effectiveness of large-scale food fortification (LSFF) of staple foods to prevent micronutrient deficiencies in high-income settings has been demonstrated, its effectiveness in LMICs is less well characterized. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does large-scale food fortification (LSFF) of staple foods prevent micronutrient deficiencies in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs)?
Study design:
This review article included 50 studies.
4 studies for vitamin A fortification with a mean intervention duration of 14 months (12 to 24 months). Geographic locations included Indonesia, South Africa, Guatemala and Nicaragua and food vehicles included sugar, maize flour and oil.
11 studies for iodine fortification. Study populations consisted mostly of school-age children and adolescents (aged 5-18 years) in Asian and African locations. Iodine fortificants were varied and included potassium iodate, sodium iodide and multiple fortificants. Intervention duration ranged from 10 months to 14 years, with a mean of 5.7 years.
19 studies for iron fortification. The study populations consisted of women and children of varying age groups, including 2 studies pertaining specifically to pregnant women and 1 looking at the effects of fortification on anaemic children.
The food vehicles were varied and included maize flour, wheat flour, rice, soy sauce, fish sauce and milk.
Several fortificants were used, including sodium iron ethylenediaminetetraacetate (NaFeEDTA), ferrous sulfate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous bisglycinate, electrolytic iron and ferric orthophosphate.
The studies were geographically diverse, with the majority coming from Asia and South America. One was a multicountry study, reporting on anemia prevalence in 12 different countries.
Intervention duration ranged from 18 months to 16 years, with a mean of 5.3 years.
17 studies for folic acid fortification. The vast majority of studies took place in Central and South America and food vehicles included wheat and maize flour.
Intervention duration ranged from 12 months to 11 years, with a mean of 4.2 years.
The range of each age group was children (1-4 years), school-age children (5-9 years), adolescents (10-19 years) and women of reproductive age (WRA).
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found in pooled analysis that vitamin A fortification was associated with a significant increase in serum retinol [SMD = 0.31, 95% CI = 0.18 to 0.45].
The effect was significant for each of the age groups assessed and particularly for older [children SMD = 0.50, 95% CI = 0.16 to 0.85].
Single studies examining the effect of vitamin A fortification in children aged 1 y and women of reproductive age also signaled improvements in serum retinol (vitamin A level in blood).
The investigators found that serum retinol levels of children aged 0-9 years significantly improved by 0.28 μg/dL [95% CI = 0.14 to 0.43 μg/dL] following large-scale food fortification with vitamin A for an average of 14 months.
Today, the global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency (VAD; defined as a serum retinol concentration 0.70 μmol/L) for children aged 5 y is 33.3%, equating to 190 million children. When considering the impact of these findings on a population curve, this global deficiency would shift to 32.82%, indicating an approximate reduction in vitamin A deficiency for 2.7 million children [95% CI = 1.3 to 4.1 million children] in just over 1 year.
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with iodine was associated with a significant increase in urinary iodine [SMD = 1.02, 95% CI = 0.63 to 1.42].
Subgroup analysis revealed a statistically significant impact for school-age children [SMD = 1.12, 95% CI = 0.57 to 1.67]. Accordingly, the prevalence of iodine deficiency was reduced for this age group as well [RR = 0.25, 95% CI = 0.21 to 0.29].
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with iodine significantly reduced goiter prevalence (grade 1-2) among school-age children with 74% [OR = 0.26, 95% CI = 0.16 to 0.43], a finding that was indicative of the long-term impact of salt iodization programs.
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with iron was associated with a small, but significant, increase in the hemoglobin concentration for combined populations (preschool children, school-age children and WRA only). However, when disaggregating by age and status (pregnant and anaemic populations at baseline) the effect remained significant for pregnant women only [SMD = 0.12, 95% CI = 0.01 to 0.23].
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with iron was associated with a 34% decline in anemia prevalence for combined age groups [RR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.59 to 0.74], with the greatest impact noted for women of reproductive age [RR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.58, 0.76], followed by school-age children (1-4 years) [RR = 0.68, 95% CI = 0.52, 0.90].
The investigators found in 3 studies looked at the impact of iron fortification in pregnant women specifically that, although anemia prevalence was significantly reduced [RR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.64 to 0.84], the decline was less than it was for nonpregnant women.
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with iron significantly increased serum ferritin increased by 0.39 μg/L [95% CI = 0.34 to 0.44 μg/L], indicating a significant improvement in iron stores for combined age groups following iron fortification.
Variability around the point estimates for serum ferritin was largest for the youngest children [SMD = 0.47, 95% CI = 0.35 to 0.59].
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with iron significantly decreased prevalence of iron deficiency by 58% among all population subsets [RR = 0.42, 95% CI = 0.32 to 0.56].
The investigators found large-scale food fortification with folic acid significantly reduced prevalence of total neural tube defects with 41% [OR = 0.59, 95% CI = 0.49 to 0.70] and neural tube defect subtype, including spina bifida with 34% [OR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.53 to 0.82], anencephaly with 51% [RR = 0.49, 95% CI = 0.40 to 0.60] and cephalocele with 36% [OR = 0.64, 95% CI = 0.47 to 0.88].
The investigators found among women of reproductive age, folic acid fortification of flour was associated with a significant decline of 80% in the prevalence of folate deficiency [RR = 0.20, 95% CI = 0.15 to 0.25], as well as improvements in serum/plasma folate levels [SMD = 1.25, 95% CI = 0.50 to 1.99].
The investigators concluded that large-scale food fortification has a positive impact on some functional health outcomes, including goiter, anemia and neural tube defects prevalence. Large-scale food fortification also increases relevant micronutrient biomarker concentrations, and improves iron stores and reduces iron deficiency prevalence in both women and children.
Original title:
Improved micronutrient status and health outcomes in low- and middle-income countries following large-scale fortification: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis by Keats EC, Neufeld LM, […], Bhutta ZA.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6537942/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on food fortification/malnutrition, vitamin A, iron, folic acid and iodine right here.