Objectives:
Do dietary calcium intakes or calcium supplements increase risk of cardiovascular disease?
Study design:
This review article included 26 prospective cohort studies and 16 RCTs.
Results and conclusions:
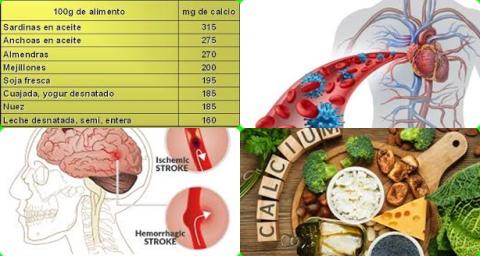
The investigators found in cohort studies that dietary calcium intakes ranging from 200 to 1500 mg/d did not affect the risk of cardiovascular disease [relative risk = 0.96, 95% CI = 0.87 to 1.05].
The investigators found in cohort studies that dietary calcium intakes ranging from 200 to 1500 mg/d did not affect the risk of coronary heart disease [relative risk = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.88 to 1.08].
The investigators found in cohort studies that dietary calcium intakes ranging from 200 to 1500 mg/d did not affect the risk of stroke [relative risk = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.85 to 1.04].
The investigators found in RCTs that calcium supplements significantly increased risk of coronary heart disease with 20% [relative risk = 1.20, 95% CI = 1.08 to 1.33, I2 = 0.0%].
The investigators found in RCTs that calcium supplements significantly increased risk of myocardial infarction with 21% [relative risk = 1.21, 95% CI = 1.08 to 1.35, I2 = 0.0%].
The investigators concluded that 200-1500 mg/d calcium intake from dietary sources do not increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including coronary heart disease and stroke, while calcium supplements increase coronary heart disease risk, especially myocardial infarction.
Original title:
The Evidence and Controversy Between Dietary Calcium Intake and Calcium Supplementation and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies and Randomized Controlled Trials by Yang C, Shi X, […], Sun G.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31625814/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on calcium and lowering of blood pressure right here.