Objectives:
Epidemiological studies have provided controversial evidence between beverage consumption and the risk of ulcerative colitis (UC). Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Is there a relationship between beverage consumption and risk of ulcerative colitis?
Study design:
This review article included 13 case-control studies and 3 prospective cohort studies, with a total of 3,689 cases (subjects with ulcerative colitis) and 335,339 controls (subjects without ulcerative colitis).
Egger test detected no significant publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
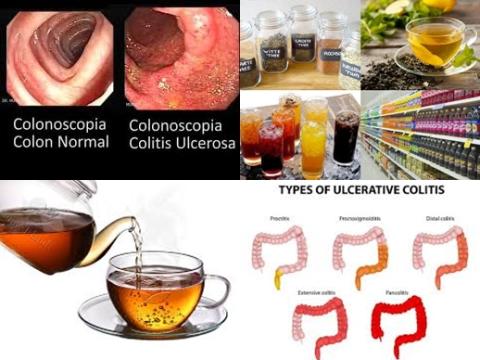
The investigators found high intake of soft drinks versus low intake, significantly increased risk of ulcerative colitis with 69% [pooled RR = 1.69, 95% CI = 1.24-2.30, I2 = 12.9%, p = 0 .332].
In subgroup analysis, no substantial changes of the primary result were found between subgroups.
The investigators found high tea consumption versus low consumption, significantly decreased risk of ulcerative colitis with 31% [pooled RR = 0.69, 95% CI = 0.58-0.83, I2 = 0.0%, p = 0 .697].
In subgroup analysis, no substantial changes of the primary result were found between subgroups.
The investigators found no significant association between alcohol [pooled RR = 1.08, 95% CI = 0.66-1.51] or coffee consumption [pooled RR = 0.58, 95% CI = 0.33-1.05, I2 = 87.5%, p 0.001] and risk of ulcerative colitis. No significant association because RR of 1 was found in the 95% CI of 0.66 to 1.51. RR of 1 means no risk/association.
The investigators concluded high consumption of soft drinks increases the risk of ulcerative colitis, while high tea consumption decreases the risk.
Original title:
Beverage consumption and risk of ulcerative colitis. Systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies by Nie JY and Zhao Q.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5728934/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on chronic disease, alcohol and tea consumption right here.