Objectives:
Does a high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) increase risk of severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients?
Study design:
This review article included 38 articles with a total of 5,699 patients with severity outcomes and 6,033 patients with mortality outcomes.
Results and conclusions:
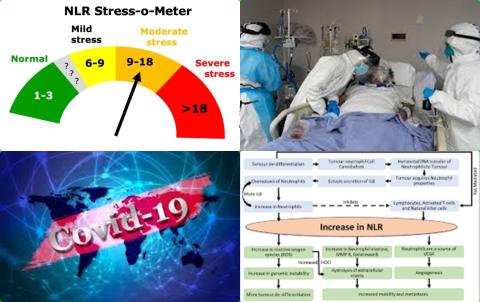
The investigators found meta-analysis showed that severe and non-survivors of COVID-19 had higher on-admission NLR levels than non-severe and survivors [SMD = 0.88, 95% CI = 0.72 to 1.04, I2 = 75.52% and SMD = 1.87, 95% CI = 1.25 to 2.49, I2 = 97.81%], respectively.
The investigators found regardless of the different NLR cut-off values, the pooled mortality RR in patients with elevated vs. normal NLR levels was 2.74 [95% CI = 0.98 to 7.66].
The investigators concluded high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) levels on admission are associated with severe COVID-19 and mortality. Further studies need to focus on determining the optimal cut-off value for neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio before clinical use.
Original title:
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on admission to predict the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis by Simadibrata DM, Calvin J, […], Ibrahim NAA.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33453617/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on coronavirus right here.