Objectives:
The associations between dietary intakes and circulating blood levels of methionine, choline or betaine and breast cancer risk remain currently unclear. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Do higher dietary intakes and circulating blood levels of methionine, choline or betaine reduce breast cancer risk?
Study design:
This review article included 8 prospective cohort studies and 10 case-control studies.
Results and conclusions:
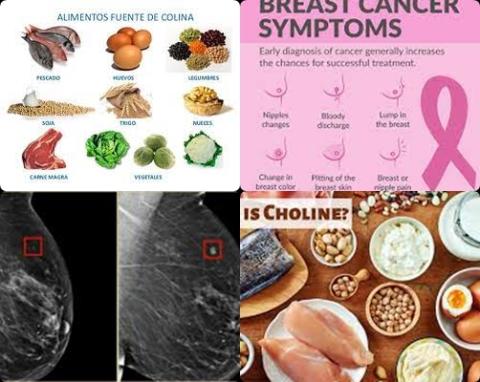
The investigators found in case-control studies that higher dietary choline intake significantly reduced breast cancer risk with 62% [OR = 0.38, 95% CI = 0.16 to 0.86].
However, this reduced risk was not significant in prospective cohort studies [HR = 1.01, 95% CI = 0.92 to 1.12].
The investigators concluded that higher choline dietary intake may reduce breast cancer risk. May reduce because this reduced risk is not found in cohort studies.
Original title:
The association between dietary intakes of methionine, choline and betaine and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis by Van Puyvelde H, Dimou N, […], De Bacquer D.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36701983/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on cohort studies/significantly, choline and breast cancer right here.