Objectives:
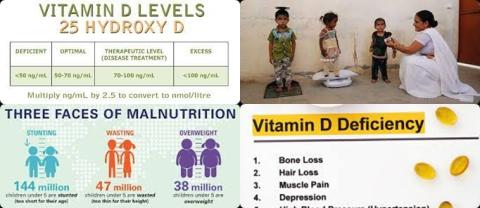
Undernutrition, defined as stunting, wasting and underweight, still implicates millions of infants and children worldwide. Micronutrients have pivotal effects on growth rate. The outcomes of vitamin D deficiency on undernutrition indices have stayed controversial. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does a low vitamin D status/level increase risk of wasting, stunting and underweight in children?
Study design:
This review article included 7 observational studies (4 cohorts and 3 cross-sectional) with a total number of 7,624 children, some of who were stunted (n = 1,349), wasted (n = 505) and underweight (n = 417).
Evidence of publication bias was not recognized in both the egger test and funnel plot for wasting [p = 0.93], stunting [p = 0.20] and underweight [p = 0.97].
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found that low vs. high serum level of vitamin D was directly significantly associated with a 30% higher risk of wasting [Summary Risk Estimate = 1.30, 95% CI =1.04 to 1.62, I2 = 0%].
However, there is no significant association between vitamin status and risk of stunting [Summary Risk Estimate = 1.10, 95% CI = 0.72 to 1.70, I2 = 81.6%] and underweight [Summary Risk Estimate = 1.12, 95% CI = 0.81 to 1.56, I2 = 49.2%].
The investigators found, according to the sensitivity analysis test results, any studies could not significantly influence summary risk regarding the association of low vs. high serum concentrations of vitamin D and risk of wasting, stunting and underweight.
The investigators concluded that when comparing low and high serum vitamin D concentration categories, there is an inverse link between vitamin D status and wasting, but no relationship with stunting as well as underweight. These findings propose that strategies to enhance vitamin D status in children by food fortification or supplementation could help the Ministry of Health's efforts to decrease undernutrition, especially wasting.
Original title:
Association Between Vitamin D Status and Undernutrition Indices in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies by Song C, Sun H, […],Lu H.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8211725/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on RCTs/cohort/significantly/review article, vitamin D and food fortification/malnutrition right here.