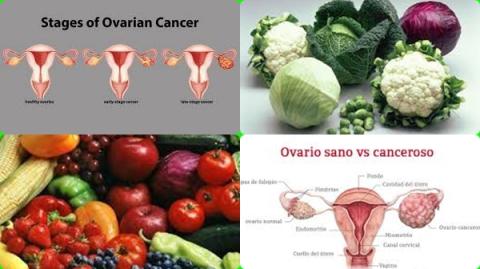
Fat, cholesterol and vitamin A increase ovarian cancer
Objectives:
It is unclear how dietary intake influences the ovarian cancer. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Is there a relationship between dietary intake of different nutrients/food groups and ovarian cancer risk?
Study design:
This review article included 97 cohort studies.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found no significant association between dietary intake and risk of ovarian cancer.
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of green leafy vegetables significantly reduced risk of ovarian cancer with 9% [RR = 0.91, 95% CI = 0.85 to 0.98].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of allium vegetables significantly reduced risk of ovarian cancer with 21% [RR = 0.79, 95% CI = 0.64 to 0.96].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of fiber significantly reduced risk of ovarian cancer with 11% [RR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.81 to 0.98].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of flavonoids significantly reduced risk of ovarian cancer with 17% [RR = 0.83, 95% CI = 0.78 to 0.89].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of green tea significantly reduced risk of ovarian cancer with 39% [RR = 0.61, 95% CI = 0.49 to 0.76].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of tota fat significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer with 10% [RR = 1.10, 95% CI = 1.02 to 1.18].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of saturated fat significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer with 11% [RR = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.01 to 1.22].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of saturated fatty acid significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer with 19% [RR = 1.19, 95% CI = 1.04 to 1.36].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of cholesterol significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer with 13% [RR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.04 to 1.22].
The investigators found in subgroup analyses that dietary intake of retinol (vitamin A) significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer with 14% [RR = 1.14, 95% CI = 1.00 to 1.30].
The investigators found, in addition, acrylamide, nitrate, water disinfectants and polychlorinated biphenyls were significantly associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The investigators concluded that dietary intakes of green leafy vegetables, allium vegetables, fiber, flavonoids and green tea reduce ovarian cancer.
Original title:
Association between dietary intake and risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis by Khodavandi A, Alizadeh F and Razis AFA.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32661683/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on different food groups and cancer right here.