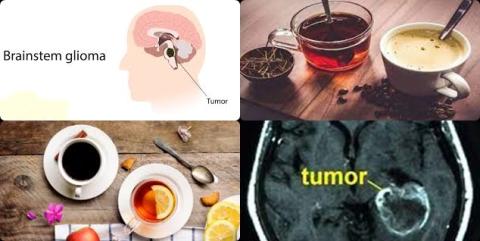
Coffee and tea consumption reduce glioma
Objectives:
Does coffee or tea consumption reduce the risk of glioma?
Study design:
This review article included 12 unique studies (cohort and case-control studies) comprising of 1,960,731 participants with 2,987 glioma cases.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found in pooled analyses that higher tea consumption was significantly associated with a lower risk of 16% for glioma [RR = 0.84, 95% CI = 0.71 to 0.98, p = 0.030, I2 = 16.42%].
The investigators found in cohort studies that higher coffee consumption was significantly associated with a lower risk of 15% for glioma [RR = 0.85, 95% CI = 0.72 to 1.00, p = 0.046, I2 = 0%].
The investigators found in cohort studies that higher tea consumption was significantly associated with a lower risk of 19% for glioma [RR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.70 to 0.93, p = 0.004, I2 = 0%].
The investigators found in dose-response meta-analysis that every one cup of coffee per day significantly decreased the risk of glioma by 3% [RR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.94 to 0.99, p = 0.016, p non-linearity = 0.054].
The investigators found in dose-response meta-analysis that every one cup of tea per day significantly decreased the risk of glioma by 3% [RR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.94 to 1.00, p = 0.048].
The investigators found meta-regression showed that the association between coffee and glioma was reduced by smoking [p = 0.029].
The investigators concluded both coffee (at least one cup of coffee per day) and tea consumption (at least one cup of tea per day) reduce the risk of glioma.
Original title:
Coffee and tea consumption and the risk of glioma: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis by Pranata R, Feraldho A, […], July J.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33750490/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on coffee and tea consumption and cancer right here.
Glioma is a type of tumor that occurs in the brain and spinal cord. About 33 percent of all brain tumors are gliomas, which originate in the glial cells that surround and support neurons in the brain, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells.
Gliomas can affect all ages, but they are most often seen in adults. Gliomas are slightly more likely to occur in men than in women and more common in Caucasians than in African Americans.