Objectives:
Evidence suggests that vitamin C supplementation could be a potential therapy in type 2 diabetes. However, its effectiveness and evidence quality require further evaluation. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does oral vitamin C supplementation improve glycemic control, cardiovascular risk factors and oxidative stress in people with type 2 diabetes?
Study design:
This review article included 28 RCTs with in totaal 1,574 participants.
RCTs were predominantly short term (6 months) with a small number of participants (n 100).
Results and conclusions:
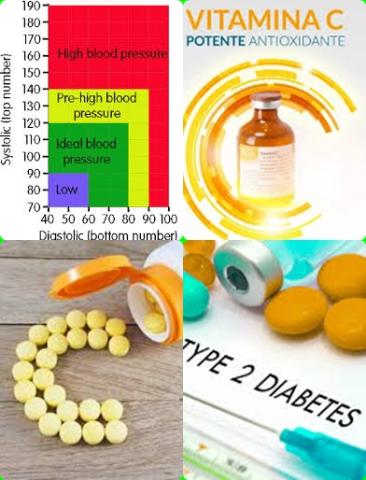
The investigators found that oral vitamin C supplementation significantly reduced systolic blood pressure [mean difference = -6.27, 95% CI = -9.60 to -2.96 mmHg, p = 0.0002, with moderate evidence certainty].
The investigators found that oral vitamin C supplementation significantly reduced HbA1c levels [mean difference = -0.54%, 95% CI = -0.90 to -0.17, p = 0.004, with very low evidence certainty].
The investigators found that oral vitamin C supplementation significantly reduced diastolic blood pressure [mean difference = -3.77, 95% CI = -6.13 to -1.42 mmHg, p = 0.002, with very low evidence certainty].
The investigators concluded evidence from short-term RCTs suggests that oral vitamin C supplementation may improve glycemic control and blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes. However, vitamin C supplementation cannot currently be recommended as a therapy until larger, long-term and high-quality trials confirm these findings.
Original title:
Effects of Vitamin C Supplementation on Glycemic Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in People With Type 2 Diabetes: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials by Mason SA, Keske MA and Wadley GD.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33472962/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on vitamin C, reducing blood pressure and diabetes right here.