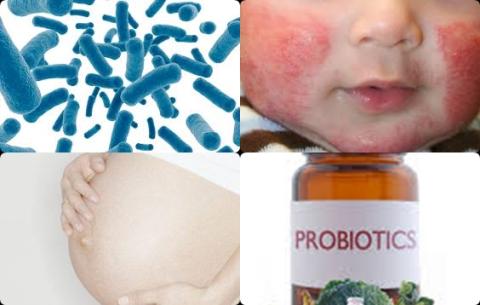
Probiotic supplementation during both prenatal and postnatal period reduces atopic dermatitis
Objectives:
Probiotic supplementation in early life may be effective in preventing atopic dermatitis (AD); however, results regarding efficacy have been controversial. Therefore, this meta-analysis (systematic review) has been conducted.
Does probiotic supplementation in early life prevent atopic dermatitis in infants and children?
Study design:
This review article included 28 RCTs.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found compared with controls, probiotic supplementation of mother was associated with a significantly reduced risk of 31% for atopic dermatitis in infants and children [OR = 0.69, 95% CI = 0.58-0.82, p 0.0001].
The investigators found compared with controls, the use of probiotics of mother during both the prenatal and the postnatal period significantly reduced the incidence of atopic dermatitis in infants and children with 33% [OR = 0.67, 95% CI = 0.54-0.82].
However, analysis of studies of probiotics given prenatally only or postnatally only did not reach statistical significance.
The investigators concluded that probiotic supplementation of mother during both the prenatal and the postnatal period reduces the incidence of atopic dermatitis in infants and children. These findings suggest that starting probiotic treatment during gestation and continuing through the first 6 months of the infant's life may be of benefit in the prevention of atopic dermatitis.
Original title:
Probiotic Supplementation for Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis by Li L, Han Z, […], He C.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30465329
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on protbiotics and pregnancy right here.