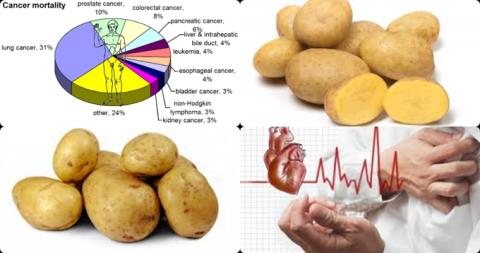
Diet with high total antioxidant capacity decreases cancer mortality

Objectives:
No conclusive information is available about the association between dietary total antioxidant capacity (DTAC) and risk of mortality. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does dietary total antioxidant capacity (DTAC) reduce risk of death from all-cause (all-cause mortality), cancer (cancer mortality) and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs mortality)?
Study design:
This review article included 5 prospective cohort studies with a follow-up period of 4.3-16.5 years. There were 38,449 deaths from all-cause, 4,470 from cancer and 2,841 from cardiovascular diseases among 226,297 individuals.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found dietary total antioxidant capacity significantly reduced all-cause mortality with 38% [combined effect size = 0.62, 95% CI = 0.60-0.64].
Significant because combined effect size of 1 was not found in the 95% CI of 0.60 to 0.64. Combined effect size of 1 means no risk/association.
The investigators found dietary total antioxidant capacity significantly reduced cancer mortality with 19% [combined effect size = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.75-0.88].
Significant means that there is an association with a 95% confidence.
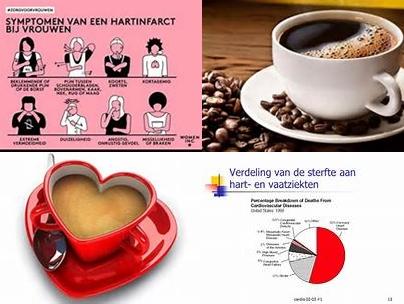
The investigators found dietary total antioxidant capacity significantly reduced cardiovascular diseases mortality with 29% [combined effect size = 0.71, 95% CI = 0.63-0.82].
The investigators found findings from linear dose-response meta-analysis revealed that a 5 mmol/day increment in dietary total antioxidant capacity based on ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) was associated with 7% and 15% lower risk of all-cause mortality, respectively.
The investigators found findings from non-linear dose-response meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in risk of all-cause mortality when increasing ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) from 2 to 12 mmol/day [p-nonlinearity = 0.002] and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) from 5 to 11 mmol/day [p-nonlinearity 0.001].
The investigators concluded a diet with high total antioxidant capacity decreases risk of death from all-cause, cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Original title:
Dietary total antioxidant capacity and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies by Parohan M, Anjom-Shoae J, […], Sadeghi O
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30756144
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on significantly/review article, antioxidant and cancer and cardiovascular diseases mortality right here.
The easiest way to get enough antioxidants from food is to eat at least 200 grams of vegetables and at least 200 grams of fruit per day.
There exist different methods to measure the antioxidant capacity of foods: Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC), Ferric Ion Reducing Power (FRAP) and Trolox Equivalence Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC). The most popular method is the ORAC determination, which was developed by the National Institutes of Health in Baltimore.
The USDA recommends an ORAC unit ingestion of about 3000 to 5000 units daily.
|
Food items |
ORAC values (micromol TE/100g) |
|
Spices, cloves, ground |
314446 |
|
Sumac, bran, raw |
312400 |
|
Spices, cinnamon, ground |
267536 |
|
Sorghum, bran, hi-tannin |
240000 |
|
Spices, oregano, dried |
200129 |
|
Spices, turmeric, ground |
159277 |
|
Sorghum, bran, black |
100800 |
|
Sumac, grain, raw |
86800 |
|
Cocoa, dry powder, unsweetened |
80933 |
|
Spices, cumin seed |
76800 |
|
Spices, parsley, dried |
74349 |
|
Sorghum, bran, red |
71000 |
|
Spices, basil, dried |
67553 |
|
Baking chocolate, unsweetened, squares |
49926 |
|
Spices, curry powder |
48504 |
|
Sorghum, grain, hi-tannin |
45400 |
|
Chocolale, dutched powder |
40200 |
|
Sage, fresh |
32004 |
|
Spices, mustard seed, yellow |
29257 |
|
Spices, ginger, ground |
28811 |
|
Spices, pepper, black |
27618 |
|
Thyme, fresh |
27426 |
|
Marjoram, fresh |
27297 |
|
Rice bran, crude |
24287 |
|
Spices, chili powder |
23636 |
|
Sorghum, grain, black |
21900 |
|
Candies, chocolate, dark |
20823 |
|
Candies, semisweet chocolate |
18053 |
|
Nuts, pecans |
17940 |
|
Spices, paprika |
17919 |
|
Chokeberry, raw |
16062 |
|
Tarragon, fresh |
15542 |
|
Ginger root, raw |
14840 |
|
Elderberries, raw |
14697 |
|
Sorghum, grain, red |
14000 |
|
Peppermint, fresh |
13978 |
|
Oregano, fresh |
13970 |
|
Nuts, walnuts, english |
13541 |
|
Nuts, hazelnuts or filberts |
9645 |
|
Cranberries, raw |
9584 |
|
Pears, dried to 40% moisture (purchased in Italy) |
9496 |
|
Savory, fresh |
9465 |
|
Artichokes, Ocean Mist, boiled |
9416 |
|
Artichokes, Ocean Mist, Microwaved |
9402 |
|
Beans, kidney, red, mature seeds, raw |
8459 |
|
Beans, pink, mature seeds, raw |
8320 |
|
Beans, black, mature seeds, raw |
8040 |
|
Nuts, pistachio nuts, raw |
7983 |
|
Currants, european black, raw |
7960 |
|
Beans, pinto, mature seeds, raw |
7779 |
|
Plums, black diamond, with peel, raw |
7581 |
|
Candies, milk chocolate |
7528 |
|
Lentils, raw |
7282 |
|
Agave, dried (Southwest) |
7274 |
|
Apples, dried to 40% moisture (purchsed in Italy) |
6681 |
|
Spices, garlic powder |
6665 |
|
Artichokes, (globe or french), raw |
6552 |
|
Blueberries, raw |
6552 |
|
Plums, dried (prunes), uncooked |
6552 |
|
Beans, black turtle soup, mature seeds, raw |
6416 |
|
Sorghum, bran, white |
6400 |
|
Chocolate syrup |
6330 |
|
Plums, raw |
6259 |
|
Babyfood, fruit, peaches |
6257 |
|
Lemon balm, leaves, raw |
5997 |
|
Soybeans, mature seeds, raw |
5764 |
|
Spices, onion powder |
5735 |
|
Blackberries, raw |
5347 |
|
Garlic, raw |
5346 |
|
Coriander (cilantro) leaves, raw |
5141 |
|
Alcoholic Beverage, wine, table, red, Cabernet Suavignon |
5034 |
|
Raspberries, raw |
4882 |
|
Babyfood, fruit, apple and blueberry, junior |
4822 |
|
Basil, fresh |
4805 |
|
Nuts, almonds |
4454 |
|
Dill weed, fresh |
4392 |
|
Cowpeas, common (blackeyes, crowder, southern), mature seeds, raw |
4343 |
|
Apples, Red Delicious, raw. with skin |
4275 |
|
Peaches, dried to 40% moisture (purchased in Italy) |
4222 |
|
Raisins, white, dried to 40% moisture (purchased in Italy) |
4188 |
|
Babyfood, fruit, applesauce, strained |
4123 |
|
Apples, Granny Smith, raw, with skin |
3898 |
|
Dates, deglet noor |
3895 |
|
Alcoholic beverage, wine, table, red |
3873 |
|
Strawberries, raw |
3577 |
|
Peanut butter, smooth style, with salt |
3432 |
|
Currants, red, raw |
3387 |
|
Figs, raw |
3383 |
|
Cherries, sweet, raw |
3365 |
|
Gooseberries, raw |
3277 |
|
Apricots, dried to 40% moisture (purchased in Italy) |
3234 |
|
Peanuts, all types, raw |
3166 |
|
Cabbage, red, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
3145 |
|
Broccoli raab, raw |
3083 |
|
Apples, raw, with skin |
3082 |
|
Raisins, seedless |
3037 |
|
Pears, raw |
2941 |
|
Agave, cooked (Southwest) |
2938 |
|
Apples, Red Delicious, raw, without skin |
2936 |
|
Juice, Blueberry |
2906 |
|
Apples, Gala, raw, with skin |
2828 |
|
Spices, cardamom |
2764 |
|
Apples, Golden Delicious, raw, with skin |
2670 |
|
Babyfood, fruit, bananas |
2658 |
|
Apples, Fuji, raw, with skin |
2589 |
|
Apples, raw, without skin |
2573 |
|
Babyfood, fruit, peaches, junior |
2551 |
|
Guava, white-fleshed |
2550 |
|
Dates, medjool |
2387 |
|
Broccoli, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
2386 |
|
Lettuce, red leaf, raw |
2380 |
|
Juice, Concord grape |
2377 |
|
Cereals, ready-to-eat, corn flakes |
2359 |
|
Juice, Pomegranate, 100% |
2341 |
|
Cereals, oats, instant, fortified, plain, dry |
2308 |
|
Cereals ready-to-eat, granola, low-fat, with raisins |
2294 |
|
Cabbage, red, raw |
2252 |
|
Apples, Golden Delicious, raw, without skin |
2210 |
|
Sorghum, grain, white |
2200 |
|
Radish seeds, sprouted, raw |
2184 |
|
Cereals ready-to-eat, oat bran |
2183 |
|
Cereals ready-to-eat, toasted oatmeal |
2175 |
|
Cereals, oats, quick, uncooked |
2169 |
|
Asparagus, raw |
2150 |
|
Cereals ready-to-eat, oatmeal, toasted squares |
2143 |
|
Sweet potato, cooked, baked in skin, without salt |
2115 |
|
Bread, butternut whole grain |
2104 |
|
Chives, raw |
2094 |
|
Cabbage, savoy, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
2050 |
|
Prune juice, canned |
2036 |
|
Guava, red-fleshed |
1990 |
|
Applesauce, canned, unsweetened, without added ascorbic acid |
1965 |
|
Bread, pumpernickel |
1963 |
|
Nuts, cashew nuts, raw |
1948 |
|
Beet greens, raw |
1946 |
|
Avocados, Hass, raw |
1933 |
|
Pears, green cultivars, with peel, raw |
1911 |
|
Rocket, raw |
1904 |
|
Oranges, raw, navels |
1819 |
|
Peaches, raw |
1814 |
|
Juice, red grape |
1788 |
|
Cabbage, black, cooked |
1773 |
|
Beets, raw |
1767 |
|
Pears, red anjou, raw |
1746 |
|
Snacks, popcorn, air-popped |
1743 |
|
Radishes, raw |
1736 |
|
Cereals, oats, old fashioned, uncooked |
1708 |
|
Tortilla chips, reduced fat, Olestra - TEMPORARY |
1704 |
|
Nuts, macadamia nuts, dry roasted, without salt added |
1695 |
|
Spinach, frozen, chopped or leaf, unprepared |
1687 |
|
Potatoes, Russet, flesh and skin, baked |
1680 |
|
Asparagus, cooked, boiled, drained |
1644 |
|
Tangerines, (mandarin oranges), raw |
1620 |
|
Broccoli raab, cooked |
1552 |
|
Grapefruit, raw, pink and red, all areas |
1548 |
|
Onions, red, raw |
1521 |
|
Beans, navy, mature seeds, raw |
1520 |
|
Cereals ready-to-eat, QUAKER, QUAKER OAT LIFE, plain |
1517 |
|
Spinach, raw |
1515 |
|
Alfalfa seeds, sprouted, raw |
1510 |
|
Juice, Cranberry/Concord grape |
1480 |
|
Lettuce, green leaf, raw |
1447 |
|
Lettuce, butterhead (includes boston and bibb types), raw |
1423 |
|
Bread, mixed-grain (includes whole-grain, 7-grain) |
1421 |
|
Nuts, brazilnuts, dried, unblanched |
1419 |
|
Broccoli, raw |
1362 |
|
Potatoes, red, flesh and skin, baked |
1326 |
|
Potatoes, russet, flesh and skin, raw |
1322 |
|
Bread, Oatnut |
1318 |
|
Cereals ready-to-eat, wheat, shredded, plain, sugar and salt free |
1303 |
|
Parsley, raw |
1301 |
|
Milk, chocolate, fluid, commercial, reduced fat |
1263 |
|
Grapes, red, raw |
1260 |
|
Tea, green, brewed |
1253 |
|
Agave, raw (Southwest) |
1247 |
|
Grapefruit juice, white, raw |
1238 |
|
Lemon juice, raw |
1225 |
|
Onions, yellow, sauteed |
1220 |
|
Kiwi, gold, raw |
1210 |
|
Olive oil, extra-virgin |
1150 |
|
Potatoes, white, flesh and skin, baked |
1138 |
|
Tea, brewed, prepared with tap water |
1128 |
|
Grapes, white or green, raw |
1118 |
|
Apricots, raw |
1115 |
|
Potatoes, red, flesh and skin, raw |
1098 |
|
Potatoes, white, flesh and skin, raw |
1058 |
|
Onions, raw |
1034 |
|
Alcoholic beverage, wine, table, rose |
1005 |
|
Mangos, raw |
1002 |
|
Juice, strawberry |
1002 |
|
Sauce, ready-to-serve, salsa |
1001 |
|
Peppers, sweet, orange, raw |
984 |
|
Peppers, sweet, yellow, raw |
965 |
|
Lettuce, cos or romaine, raw |
963 |
|
Soybeans, mature seeds, sprouted, raw |
962 |
|
Eggplant, raw |
933 |
|
Peppers, sweet, green, raw |
923 |
|
Beans, pinto, mature seeds, cooked, boiled, without salt |
904 |
|
Sweet potato, raw, unprepared |
902 |
|
Pineapple, raw, extra sweet variety |
884 |
|
Kiwi fruit, (chinese gooseberries), fresh, raw |
882 |
|
Bananas, raw |
879 |
|
Juice, cranberrry, 100% - cranberry blend, red |
865 |
|
Onions, white, raw |
863 |
|
Cabbage, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
856 |
|
Chickpeas (garbanzo beans, bengal gram), mature seeds, raw |
847 |
|
Peppers, sweet, red, sauteed |
847 |
|
Raisins, white, fresh (purchased in Italy) |
830 |
|
Cauliflower, raw |
829 |
|
Lime juice, raw |
823 |
|
Grape juice, white |
793 |
|
Peppers, sweet, red, raw |
791 |
|
Olive oil, extra-virgin, w/parsley, home prepared |
766 |
|
Sweet potato, cooked, boiled, without skin |
766 |
|
Beans, snap, green, raw |
759 |
|
Nectarines, raw |
750 |
|
Peas, yellow, mature seeds, raw |
741 |
|
Chilchen (Red Berry Beverage) (Navajo) |
740 |
|
Corn, sweet, yellow, raw |
728 |
|
Orange juice, raw |
726 |
|
Pear juice, all varieties |
704 |
|
Peppers, sweet, yellow, grilled |
694 |
|
Tomato products, canned, sauce |
694 |
|
Mush, blue corn with ash (Navajo) |
684 |
|
Olive oil, extra-virgin, w/basil, home prepared |
684 |
|
Carrots, raw |
666 |
|
Cauliflower, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
620 |
|
Nuts, pine nuts, dried |
616 |
|
Peppers, sweet, green, sauteed |
615 |
|
Onions, sweet, raw |
614 |
|
Peas, green, frozen, unprepared |
600 |
|
Catsup |
578 |
|
Pineapple juice, canned, unsweetened, without added ascorbic acid |
568 |
|
Vinegar, Apple |
564 |
|
Pineapple, raw, traditional varieties |
562 |
|
Olive oil, extra-virgin, w/garlic, home prepared |
557 |
|
Vegetable juice cocktail, canned |
548 |
|
Tomatoes, plum, raw |
546 |
|
Peas, split, mature seeds, raw |
524 |
|
Corn, sweet, yellow, frozen, kernels cut off cob, unprepared |
522 |
|
Cabbage, raw |
508 |
|
Celery, raw |
497 |
|
Broccoli, frozen, spears, unprepared |
496 |
|
Leeks, (bulb and lower leaf-portion), raw |
490 |
|
Tomato juice, canned, with salt added |
486 |
|
Cocoa mix, powder |
485 |
|
Pumpkin, raw |
483 |
|
Spices, poppy seed |
481 |
|
Lettuce, iceberg (includes crisphead types), raw |
438 |
|
Carrots, baby, raw |
436 |
|
Peaches, canned, heavy syrup, drained |
436 |
|
Babyfood, juice, pear |
414 |
|
Corn, sweet, yellow, canned, brine pack, regular pack, solids and liquids |
413 |
|
Vinegar, Red wine |
410 |
|
Apple juice, canned or bottled, unsweetened, without added ascorbic acid |
408 |
|
Tomatoes, red, ripe, cooked |
406 |
|
Squash, winter, butternut, raw |
396 |
|
Alcoholic beverage, wine, table, white |
392 |
|
Pineapple, raw, all varieties |
385 |
|
Tomatoes, red, ripe, raw, year round average |
367 |
|
Carrots, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
317 |
|
Melons, cantaloupe, raw |
315 |
|
Fennel, bulb, raw |
307 |
|
Beans, snap, green variety, canned, regular pack, solids and liquids |
290 |
|
Vinegar, Apple and Honey |
270 |
|
Eggplant, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt |
245 |
|
Beans, lima, immature seeds, canned, regular pack, solids and liquids |
243 |
|
Melons, honeydew, raw |
241 |
|
Juice, cranberry, white |
232 |
|
Vinegar, Honey |
225 |
|
Olive oil, extra-virgin, w/garlic and red hot peppers, home prepared |
219 |
|
Cucumber, with peel, raw |
214 |
|
Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, raw |
180 |
|
Watermelon, raw |
142 |
|
Cucumber, peeled, raw |
126 |
|
Oil, peanut, salad or cooking |
106 |
|
Limes, raw |
82 |