Objectives:
Is there a causal relationship between strawberry consumption and positive effects on cardiovascular risk factors?
Study design:
This review article included 11 RCTs (6 for blood pressure, 7 for lipid profile, 7 for fasting blood glucose and 6 for C-reactive protein).
There was little evidence of heterogeneity in the analysis and no evidence of publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
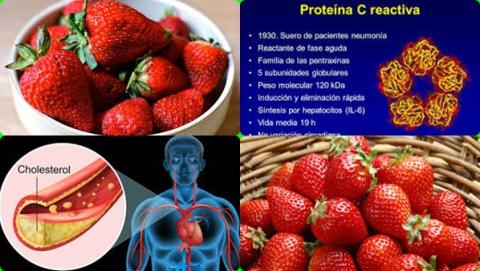
The investigators found overall, strawberry consumption significantly reduced C-reactive protein (CRP) levels by 0.63 mg/L [95% CI = -1.04 to -0.22] but did not affect blood pressure, lipid profile or fasting blood glucose in the main analyses.
The investigators found stratified by baseline endpoint levels, that strawberry consumption significantly reduced total cholesterol levels among people with baseline levels >5 mmol/L [-0.52 mmol/L, 95% CI = -088 to -0.15] and reduced LDL-cholesterol levels among people with baseline levels >3 mmol/L [-0.31 mmol/L, 95% CI = -0.60 to -0.02].
The investigators concluded strawberry consumption reduces C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and improves total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol (bad cholesterol) in individuals with high baseline levels (level at the beginning of the study).
Original title:
Effects of strawberry intervention on cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials by Gao Q, Qin LQ, […], Dong JY.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32238201
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on fruit consumption and lowering of cholesterol levels right here.