Objectives:
Several epidemiological studies have investigated the association between dietary fat intake and cardiovascular disease. However, dietary recommendations based on systematic review and meta-analysis might be more credible. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does dietary fat intake increase cardiovascular disease risk?
Study design:
This review article included 56 cohort studies.
Egger test showed no evidence of significant publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found highest versus lowest levels of total dietary fat were not associated with cardiovascular disease risk [RR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.93-1.01, I2 = 54.0%].
Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study had an excessive influence on the pooled effect.
In addition, the analysis was repeated stratified according to each covariate. The results were consistent with that observed in meta-regression.
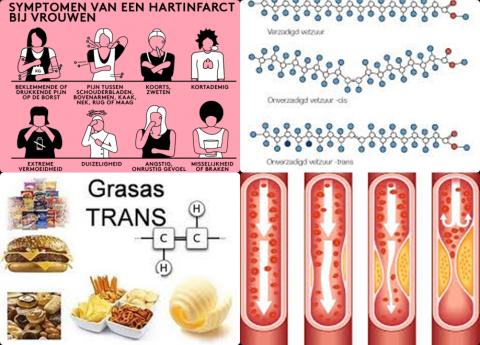
The investigators found highest versus lowest levels of dietary trans fatty acids intake were associated with a 14% increase of the risk of cardiovascular disease [RR = 1.14, 95% CI = 1.08-1.21, I2 = 26.1%].
Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study had an excessive influence on the pooled effect.
The investigators found dose-response analysis showed the risk of cardiovascular disease significantly increased with 16% [RR = 1.16, 95% CI = 1.07-1.25, p-linearity = 0.033] for an increment of 2% energy/day (2 En%/day) of dietary trans fatty acids intake.
The investigators found highest versus lowest levels of dietary saturated fatty acids intake were not associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease [RR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.93-1.02, I2 = 56.8%].
Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study had an excessive influence on the pooled effect
In addition, the analysis was repeated stratified according to each covariate. The results were consistent with that observed in meta-regression.
The investigators found highest versus lowest levels of dietary monounsaturated fatty acids intake were not associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease [RR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.93-1.01, I2 = 50.3%].
Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study had an excessive influence on the pooled effect.
In addition, the analysis was repeated stratified according to each covariate. The results were consistent with that observed in meta-regression.
The investigators found highest versus lowest levels of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids intake were not associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease [RR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.93-1.004, I2 = 55.8%].
Sensitivity analysis showed that no individual study had an excessive influence on the pooled effect.
In addition, the analysis was repeated stratified according to each covariate. The results were consistent with that observed in meta-regression.
The investigators found in studies that has been followed up more than 10 years, that dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids intake significantly reduced cardiovascular disease risk with 5% [RR = 0.95, 95% CI = 0.91-0.99, I2 = 62.4%].
The investigators concluded there is a cardio-protective effect of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids intake in studies that has been followed up more than 10 years. While, an increment of 2% energy/day (2 En%/day) of dietary trans fatty acids intake increases risk of cardiovascular disease.
Original title:
Dietary total fat, fatty acids intake, and risk of cardiovascular disease: a dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies by Zhu Y, Bo Y and Liu Y.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6451787/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on fat consumption and cardiovascular diseases right here.