Objectives:
Does type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) decrease bone mineral density (BMD) in children and adolescents?
Study design:
This review article included 9 cross-sectional studies with a total of 1,522 children and adolescents.
Funnel plot and the Egger test did not reveal significant publication bias.
Results and conclusions:
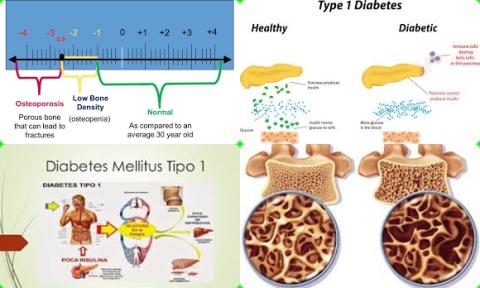
The investigators found a significant decrease in bone mineral density Z-score in the whole body [pooled WMD = -0.47, 95% CI = -0.92 to -0.02, I2 = 80.2%] and lumbar spine [pooled WMD = -0.41, 95% CI = -0.69 to -0.12, I2 = 80.3%] in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus, which was consistent in published studies from Asia and South America, but inconsistent in the North America and Europe.
Sensitivity analyses did not modify these findings.
The investigators found, importantly, the differences in bone mineral density Z-scores were independent of age, level of glucose control (HbA1c) and prepubertal stage.
The investigators concluded type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) decreases bone mineral density (BMD) Z-scores in the whole body and lumbar spine in children and adolescents.
Original title:
Association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and reduced bone mineral density in children: a meta-analysis by Zhu Q, J Xu J, […], Shi J.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33404757/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on diabetes right here.