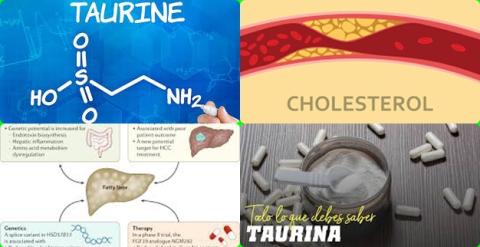
0.5 to 6 g/d taurine supplementation reduces total cholesterol and triglyceride in patients with liver dysregulation
Objectives:
Taurine plays a pivotal role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, blood pressure homeostasis and obesity largely due to its cytoprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Despite promising data from animal studies in this scenario, the efficacy of taurine supplementation in human studies has been inconsistent. Therefore, this review article has been conducted.
Does taurine supplementation lower blood pressure and improve the lipid profile in patients with liver dysregulation?
Study design:
This review article included 12 RCTs.
Most studies were conducted in patients with liver or metabolic dysregulation (diabetes, hepatitis, fatty liver, obesity, cystic fibrosis, chronic alcoholism and cardiac surgery).
The taurine dosage varied from 0.5 to 6 g/d for 15 days to 6 months.
Results and conclusions:
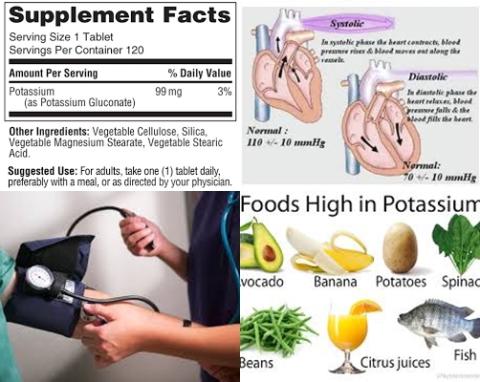
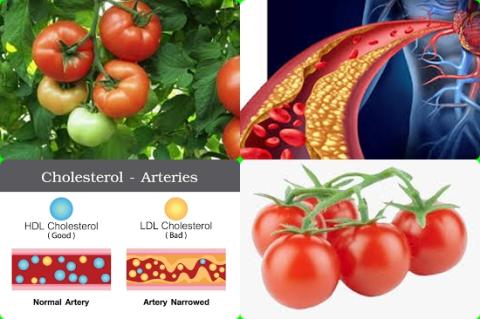
The investigators found that taurine administration (supplementation) had a significant effect of on systolic blood pressure [WMD = -4.67 mm Hg, 95% CI = -9.10 to -0.25], diastolic blood pressure [WMD = -2.90 mm Hg, 95% CI = -4.29 to -1.52], total cholesterol levels [WMD = -10.87 mg/dL, 95% CI = -16.96 to -4.79] and triglycerides levels [WMD = -13.05 mg/dL, 95% CI = -25.88 to -0.22].
The investigators found, however, that taurine administration had no effect on fasting blood glucose [WMD = 0.06 mg/dL], HDL cholesterol [WMD = 0.90 mg/dL], LDL cholesterol [WMD = -6.17 mg/dL], as well as on body mass index [WMD = -0.46 kg/m2] and body weight [WMD = -0.47 kg] as the anthropometric measures.
The investigators concluded that, in patients with liver dysregulation, taurine supplements (0.5 to 6 g/d for 15 days to 6 months) reduce blood pressure and improve the lipid profile by reducing total cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Original title:
The effects of taurine supplementation on obesity, blood pressure and lipid profile: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials by Guan L and Miao P.
Link:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32871172/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find here more information/studies about taurine consumption and lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
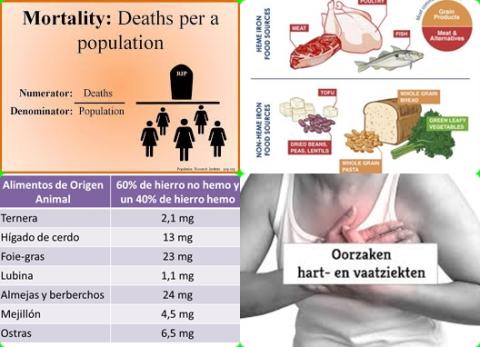
The main sources of taurine are animal foods, such as meat, fish and dairy products.