Elderly
Scientific studies (review articles) on the relationship between diet/nutrients and elderly prevention:
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a certain topic) of randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trials (RCTs) will answer the following question:
"Do taking dietary supplements make sense?" Yes for a positive conclusion and no for a negative conclusion.
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a certain topic) of cohort studies or case-control studies will answer the following question:
"Should I change my diet?".
2024:
- Daily 500mg n-3 PUFA during 12 months improve cognitive functions
- 15 g/day fish protein dietary intake may reduce fractures
2023:
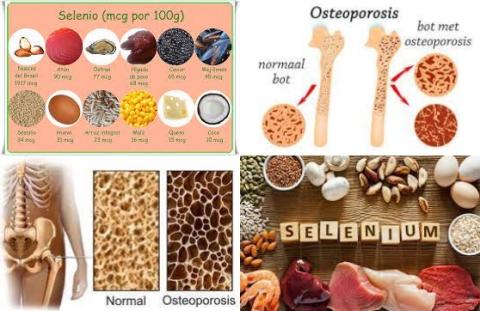
- High selenium dietary intake reduces hip fracture
- Lower serum magnesium concentrations increase fractures
- Lower blood carotenoid level is a risk factor for dementia
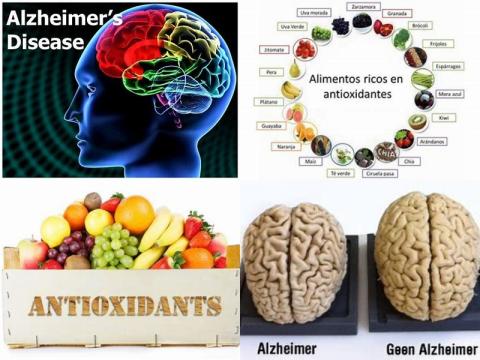
- High antioxidant dietary intake reduces Alzheimer's disease
- Fish consumption reduces Alzheimer's disease
2022:
- High dietary intake of vitamin E reduces dementia
- Skim milk, poultry and non-meat animal products reduce age-related eye disease
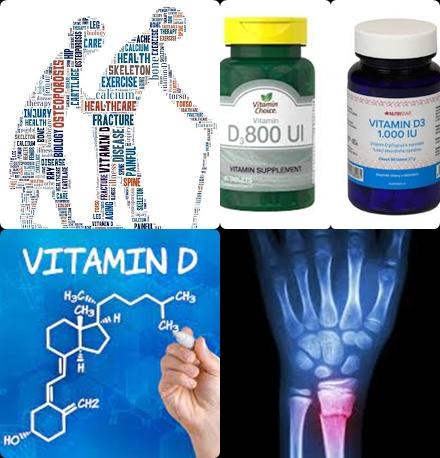
- 800-1,000 IU/d vitamin D3 reduces fracture and fall risk among elderly
- 400 IU/day to 300,000 IU vitamin D supplementation improves handgrip strength in postmenopausal women
- Higher concentration of carotenoids and vitamin E in blood reduce age-related macular degeneration
- Protein supplementation + exercise increase lower-extremity strength in healthy older Asian adults with sarcopenia
2021:
- 100 µg/d vitamin K2 + 1000 mg/d calcium supplements increase lumbar spine bone mineral
- Mushroom consumption reduces all-cause mortality
- 200-700 g/d fruits and vegetables consumption decreases frailty
- Monounsaturated fatty acids dietary intake reduces all-cause mortality
- Chair-based exercise programmes improve upper extremity and lower extremity function in older adults
- Supplementation with 320-729 mg/d magnesium may improve sleep in older adults with insomnia
- <11 g/day alcohol and <2.8 cups/day coffee reduce cognitive deficits
- Higher plasma DHA and EPA levels reduce advanced age-related macular degeneration
- Alcohol consumption increases risk of any fractures
- 0.5-50 mg/d carotenoid supplementation improves cognitive performance among healthy adults
- Daily 700-1000 mg dietary calcium intake increases cardiovascular disease in healthy postmenopausal women
- Daily egg consumption have beneficial effects on macular pigment optical density
- A high dietary intake of β-cryptoxanthin reduce osteoporosis and hip fracture
2020:
- EPA + DHA supplements for at least 6 months increase walking speed among the elderly
- 54 mg/day genistein increase bone mineral density in postmenopausal women
- Vitamin K + D supplement increase bone mineral density
- Dairy products increase bone mineral density in postmenopausal women:
- LDL cholesterol levels >121 mg/dL increase Alzheimer's disease
- Dietary intake of vitamin C-rich foods reduces risk of osteoporosis
- Higher linoleic acid blood concentration reduces cancer mortality
- Statins improve activities of daily living ability in Alzheimer disease patients
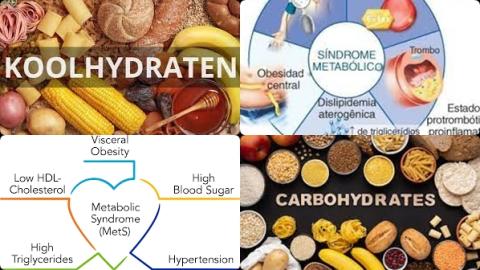
- Carbohydrate intake does not increase risk of fracture
- Middle-aged people with diabetes are at higher risk of developing dementia
2019:
- miRNAs may be a promising biomarker for Alzheimer's disease
- 1 drink or more per day increases osteoporosis
- Low folate levels increase risk of depression among the aged people
- Lower vitamin E levels increase Alzheimer's disease
- High serum uric acid level decreases risk of fractures
- Soy/soy products consumption reduce risk of mortality from cardiovascular diseases
- High homocysteine level increases Alzheimer disease
- One serving of fruits and vegetables per day reduces fractures
- Saturated fat increases Alzheimer disease
- Vegetable-based diet reduces osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
- Diet with high total antioxidant capacity decreases cancer mortality
- Potato consumption does not increase risk of mortality in adults
- Dietary intake of 5 mg/d vitamin A reduces age-related cataract
2018:
- Alzheimer's disease patients have a low plasma vitamin E level
- A diet with high antioxidant properties reduces all-cause mortality risk
- All-cause mortality risk is lowest with a diet with 50-55 En% carbohydrates
- A low selenium level in the brain increases Alzheimer’s disease
- Monounsaturated fatty acids intake derived from animal sources increase risk of fracture
- High fish consumption decreases risk of age-related macular degeneration
- Coronary heart disease and heart failure increase risk of dementia
- Inflammatory markers are associated with an increased risk of all-cause dementia
- Insulin-degrading enzyme protein level is lower in Alzheimer's disease patients
- Vitamin D level of 25 to 35 ng/mL decreases risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease
- Aerobic exercise benefits global cognition in mild cognitive impairment patients
- A high consumption of yogurt and cheese reduces hip fracture
- Regular aerobic exercise delays cognitive decline among individuals having Alzheimer's disease
2017:
- High tea consumption reduces hip fracture risk among women
- Dietary intake of n-3 PUFAs declines hip fracture risk
- Every 500 kcal increase per week reduce Alzheimer’s disease with 13%
- Higher dietary intake of vitamin A decreases total fracture risk
- A high vitamin D level increases walking speed among older adults
- Fruit and vegetables reduce risk of cognitive disorders
- Atrial fibrillation, previous stroke, myocardial infarction, hypertension, diabetes and previous TIA increase risk of post-stroke dementia
- At least 28 g/d whole grain intake reduce risk of total, cardiovascular and cancer mortality
- 50 mg/day dietary vitamin C intake decreases hip fracture risk
- At least 4 servings/week fish is associated with decreasing memory decline
- Low vitamin D status is related to poorer cognition in healthy adults
- Serum zinc/iron levels are decreased in Alzheimer's disease patients
- Circulatory selenium concentration is lower in Alzheimer's disease patients
- Higher protein intake may increase bone mineral density
- Tea consumption increases bone mineral density
- Daily 50μg vitamin K dietary intake decreases the risk of fractures
- Manganese deficiency may be a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease
- Olive oil intake reduces risk of type 2 diabetes
- Weekly 100 grams fish reduces dementia of Alzheimer type
- Long-term cheese consumption does not increase risk of all-cause mortality
- Daily 100g fruit and vegetable reduces risk of cognitive impairment and dementia among elderly
- Decreased walking pace increases risk of dementia in elderly populations
2015:
- Serum non-ceruloplasmin copper is higher in Alzheimer's disease
- At least 580 mg/day DHA or 1 g/day DHA/EPA improves memory function in older adults with mild memory complaints
2013:
2012:
- 75-87.5 nmol/L vitamin D decrease mortality in the general population
- Daily 54 mg soy isoflavone for 6 weeks to 12 months reduces the frequency and severity of hot flashes
- Diabetes increases risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment
- Dietary intakes of vitamin C and E lower risk of Alzheimer's disease
2011:
2009:
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Most developed world countries have accepted the chronological age of 65 years as a definition of elderly. The common problems in elderly are:
- High blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cancer
- Mobility and falls
- Dementia
- Osteoporosis
https://elmondo.org/en/dementia
- Decreased vision
- Pneumonia
- Deterioration of hearing
- Loss of appetite and thirst
- Muscle loss
- Malnutrition
Nutrition has a marked effect on the aging process. For example, a good nutritional status can retard the aging process while a daily energy intake below 1700 kcal can cause a deficiency of vitamins and minerals. A deficiency of vitamins and minerals can in turn accelerate the aging process.
The aging process does not begin at 65 of age, but already at 30 or even at younger age.
One consequence of elderly is the loss of muscle strength. Per year an elderly will lose around 0.25 kg muscle. Muscle loss can be counteracted by strength training (60-85% of 1RM and 3-4 times per week). Muscle loss will result in a lower resting metabolic rate.
Dietary guidelines for elderly:
- To maintain strong bones in elderly, is advisable to choose products with 15-25 En% protein or your daily diet (=the average of all meals/products that you eat on a daily basis) should look like this:
15-25 En% protein, 30-35 En% fat, of which 7-10 En% saturated fat, maximum 0.3 gram salt per 100 kcal and 1.3- 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal. The easiest way to meet this diet is to choose for meals/products with also 15-25 En% protein, 30-35 En% fat, of which 7-10 En% saturated fat, maximum 0.3 gram salt per 100 kcal and 1.3- 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal.
However, the most important factors for bone maintenance in elderly are 60-90 minutes of physical exercise (preferably strength training) per day in combination with 15-30 micrograms vitamin D and 1 gram calcium or more per day. - Stop smoking because smoking causes atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a major risk factor for developing cardiovascular diseases.
- Aim for a healthy weight. A healthy weight has a BMI of 18.5-25. BMI is weight divided by height squared (weight (kg)/height2 (m)).
- Spend at least 60-90 minutes per day on physical exercises or at least 10000 steps per day.
- Eat at least 2 times a week (100-150 g fish per time) oily fishes or take daily 250-500 mg EPA and DHA. EPA and DHA are found in fish oil supplements. However, fish oil supplements cannot match the positive effects of eating fish.
- Oily fishes are sardines, herring, salmon, anchovies, eel and mackerel.
- Eat 300 grams of vegetables and five servings of fruit per day or 30 grams of fiber per day. 10-30 grams of fiber a day decreases the LDL cholesterol levels.
- 30 grams of fiber per dag corresponds to a daily diet of minimum 1.5 grams of fiber per 100 kcal.
- Limit alcohol to 2-3 glasses for men and 1-2 glasses for women per day.
- Eat no more than 6 grams of salt per day, corresponding to 2400 mg of sodium.
- 6 grams of salt per day corresponds to a daily diet of <0.3 g salt per 100 kcal.
- Eat no more than 200 grams of cholesterol per day at an elevated LDL cholesterol level.
- Eat no more than 19 grams of saturated fat per day at 2500 kcal and 15 grams of saturated fat at 2000 kcal. The WHO advises 2000 kcal per day for women and 2500 kcal for men.
- Eat with other people because group eating can increase the appetite. Elderly people often have a poor appetite.
- Put every day 1 bottle of 2 liters of water on the table. This ensures that you’ll get enough fluid because the sensation of thirst in the elderly can be significantly reduced.
- Take daily 15-30 micrograms (600-1200 IU) of vitamin D. Take dietary supplements always in consultation with a dietitian, nutritionist or your GP!
- Take daily a multi-vitamin supplement.
- Take 500 micrograms of folic acid per day at a high homocysteine level.
- Take daily 1000 mg calcium. It can be through diet or dietary supplements.
- Do not take antioxidant supplements. They do more harm than good!
- It is preferable to obtain antioxidants through diet (200-300 grams of vegetables and 2-5 servings of fruit per day).