Pregnancy
Scientific studies (review articles) on the relationship between diet/nutrients and pregnancy:
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a specific topic) of randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trials (RCTs) will answer the following question:
"Do taking dietary supplements make sense?" Yes for a positive conclusion and no for a negative conclusion.
One swallow does not make a summer. A famous Dutch saying that could not be any more obvious. Just because one single scientific study about a certain topic makes certain claims, it does not necessarily mean it is true. On the other hand, a review article (a collection of scientific studies on a specific topic) of cohort studies or case-control studies will answer the following question:
"Should I change my diet?".
2023:
- Probiotic/synbiotic supplements improve glucose and lipid metabolism in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Vitamin B6 supplements reduce nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
2022:
2021:
- Oral magnesium supplementation does not reduce leg cramps during pregnancy
- Salt iodination alone is not sufficient to provide adequate iodine status to pregnant women
- Breastfeeding reduces ovarian cancer in women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation
- Vitamin and mineral supplementation improves glycemic control in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
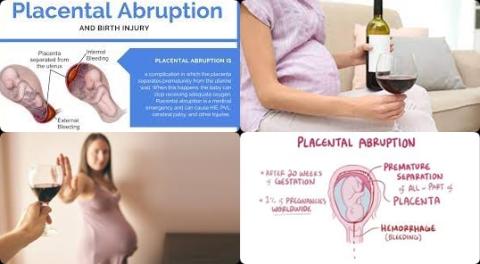
- Prenatal alcohol exposure increases placental abruption
- Preterm birth and low birthweight are strongest risk factors associated with increased case fatality of infants with spina bifida
- Enteral zinc supplementation enhances weight gain and linear growth in preterm infants
- >650 mg/day maternal or neonatal DHA and/or EPA supplements increase weight in childhood
- 400 μg folic acid during pregnancy reduce offspring's autism spectrum disorders
- Multiple-micronutrient supplementation improves birth outcomes among pregnant adolescents in low- and middle-income countries
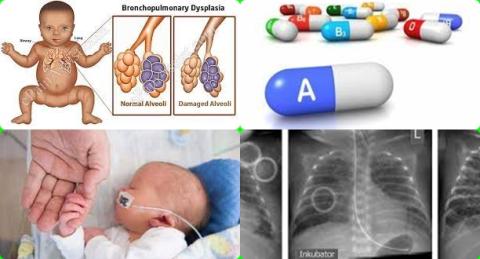
- Vitamin A supplementation reduces bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants
- CNS congenital abnormalities, intracranial calcifications, fetal loss, SGA, low birth weight and prematurity are associated with Zika virus infection
- A low maternal serum zinc level increases pre-eclampsia in African women
- Daily 100 mg cholesterol increase gestational diabetes mellitus
2020:
- Probiotic supplementation during pregnancy is beneficial for gestational age
- COVID-19 pandemic increases anxiety among women during pregnancy and perinatal period
- Coronavirus infection is more likely to affect pregnant women
- Rates of vaccine coverage immediately after birth are very low for BCG and HepB-BD in neonates in sub-Saharan Africa
- Artemisinin-based combination therapies should be treatment guidelines for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in pregnant women
- Higher levels of gestational vitamin D reduce multiple sclerosis in offspring
- Iron fortification increases haemoglobin concentration during pregnancy
- Probiotic supplementation has positive effects on outcomes of preterm infants in India
- No association between oral cholera vaccination and adverse pregnancy outcomes
- Influenza vaccination during pregnancy reduce infant influenza
- Probiotic supplementation improves outcomes of preterm infants in India
- Omega-3 fatty acids + vitamin E or D reduce gestational diabetes
- Maternal folic acid supplementation is associated with an increased birth weight
- Measles infection in pregnancy is dangerous for mother and fetus
- N-3 fatty acids supplementation reduces preeclampsia during pregnancy
- High maternal thyroid hormones during pregnancy increase neonatal birth weight
2019:
- 75 mg daily DHEA supplements increase fertility in women
- Higher plasma levels of free fatty acids increase gestational diabetes mellitus
- Pregnancy-associated malaria increases preterm birth and low birth weight
- HPV vaccination during pregnancy does not increase adverse pregnancy outcomes
- Maternal folic acid supplementation reduces childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
- Multiple micronutrient supplementation generates positive health outcomes for both infants and pregnant women
- 0.6-2 gram calcium supplement reduce gestational hypertension
- Maternal vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy increases low birth weight
- Mother-infant skin to skin contact immediately after birth increases breastfeeding
- Steady-state red blood cell folate concentrations can be reached with 375-570 µg folic acid/day
- Breastfeeding can be improved by a combination of professional and laypersons
- High prenatal vitamin D level reduces risk autism-related traits later in life
2018:
- Probiotic supplementation during both prenatal and postnatal period reduces atopic dermatitis
- 2g inositol twice daily reduce preterm delivery rate
- Antioxidant supplements could increase sperm quality
- Egg into an infant’s diet between 3 and 6 months of age reduces egg allergy risk
- PUFA supplements do not improve intelligence in low birth weight children
- Kangaroo mother care increases breastfeeding
- Antenatal care and institutional delivery increase exclusive breastfeeding practices in Ethiopia
- Asian vegetarian mothers have an increased risk to deliver babies with low birth weight
- Low maternal iodine status in early pregnancy gives lower IQ
- Myo-inositol supplementation reduces risk of gestational diabetes and preterm delivery in pregnant women
- Anemia at the beginning of pregnancy increases a SGA baby
- Maternal probiotic supplements during pregnancy and lactation reduce eczema during childhood
2017:
- First-trimester use of artemisinin derivatives is not associated with an increased risk of miscarriage or stillbirth compared to quinine
- ABT results in higher efficacy than QBT in the second and third trimester of pregnancy with uncomplicated falciparum malaria
- Women’s groups practising participatory learning and action improve key behaviours on the pathway to neonatal mortality
- Breastfeeding during 6-9 months reduces risk of endometrial cancer
- Antenatal multiple micronutrient supplements provide greater birth-outcome benefits for infants born to undernourished and anaemic pregnant women
- Plasmodium falciparum malaria in pregnancy increases stillbirth risk
- Daily 1mg heme iron increases risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant women
- Childhood nutritional supplementation with ≥5 nutrients improves cognitive development of children in developing countries
- Pregnant women with malnutrition and malaria infection are at increased risk of having a low birthweight compared to women with only 1 risk factor or none
- Severe vitamin D deficiency (<20 ng/mL) increases risk of early spontaneous pregnancy loss
- Serum ceruloplasmin may be a useful screening and follow-up tool for developing preeclampsia
- High serum copper level increase risk of preeclampsia in Asian pregnant women
- Zinc sulfate supplementation does not reduce neonatal jaundice
- Fish consumption during pregnancy is not associated with risk of asthma and other allergy-related diseases from infancy to mid childhood
- Routine supplementation of full-term infant milk formula with LCPUFA cannot be recommended
- Vitamin D supplementation alone during pregnancy reduces risk of preterm birth
- Maternal vitamin B12 deficiency increases low birth weight in newborns
2013:
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Childbirth usually occurs about 38 weeks after conception; in women who have a menstrual cycle length of four weeks, this is approximately 40 weeks from the start of the last normal menstrual period. A pregnancy of 37 to 42 weeks is considered full-term. A pregnancy less than 37 weeks is considered pre-term, which is dangerous due to underdevelopment. Over 42 weeks is also dangerous due to septic poisoning.
Women generally don't begin to feel the baby moves until sometime between 16 and 22 weeks or later. In general, the gender can be determined with certainty after the fourteenth week. After 30 weeks of gestation, the baby is able to recognize a language.
The pregnancy is divided into 3 periods:
- The first 3 months. During these months all organs of the fetus are developed.
- The second three months, in which the organs further develop.
- The last 3 months. During these 3 months the emphasis is put on growth and the unborn child gets per day 67 mg of DHA from the mother.
A woman with a BMI of 18.5-25 will gain during pregnancy about 12 kg, of which about one third is the weight of the child.
| BMI before pregnancy | Desired weight gain during pregnancy |
| <19.8 | 12 .5-18 |
| 19.8-26 | 11.5-16 |
| 26-29 | 7-11.5 |
| >29 | 6 |
| A woman with 65 kg and 1.57 meters has a BMI of 26.4 (65/(1.57x1.57)). BMI is kg/m2. | |
| Energy requirements during pregnancy | |
| The duration of pregnancy | Extra kcal per day |
| The first 3 months | 70 |
| The second three months | 260 |
| The last 3 months | 500 |
During breastfeeding mothers need on average 500 extra calories per day. Most women need 6 months to a year after childbirth to get back to their pre-pregnancy weight.
It is not desirable to lose weight during pregnancy.
The World Health Organization shows that optimal birth weight of 3.1-3.6 kg is associated with maternal weight gains of 10-14 kg.
Dietary guidelines during pregnancy:
- A balanced diet during pregnancy contains 18-24 kJ (4.3-5.7 kcal) per kg body weight. This diet has a low GI value and includes whole grains, fruits, beans and vegetables.
- Your daily diet (=all meals/products that you eat on a daily basis) should on average contain maximum 30 En% fat, maximum 7-10 En% saturated fat, 15-20 En% protein, 50-55 En% carbohydrates, maximum 25 En% simple sugars, maximum 0.3 gram salt per 100 kcal, minimum 1.3 grams of fiber per 100 kcal and fish providing 500 mg of EPA and DHA (with 200 mg DHA) per day.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Stop smoking.
- Take daily 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid supplement for a period of at least four weeks prior to the first eight weeks of pregnancy.
400 mcg of folic acid per day reduces the risk of getting a spina bifida and cleft palate in the unborn child. - Eat no more than 3000 micrograms of vitamin A per day.
- Aim for a BMI of 18.5-25 before entering the pregnancy. Research has shown that the healthiest pregnancy is associated with a pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.
- Eat fish, providing at least 200 mg of DHA per day. DHA is needed for the development of the brain and vision of the fetus.
- Do not eat raw or undercooked (pink fried) meat because the mother can be infected with toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasmosis can cause permanent damage to the brains and eyes of the unborn child. Feces of cats and sandboxes are also sources of toxoplasmosis.
- Do not eat cheeses made from raw milk (lait au cu).The listeria bacteria are found in raw milk. Listeria can be harmful to the unborn child and can even cause miscarriage.
- Take a multivitamin supplement.
- Take fish oil supplements (250-500 mg of EPA and DHA per tablet) if you do not eat fish. Take only dietary supplements after consulting an expert!
Dietary guidelines during breastfeeding:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Stop smoking.
- Do not drink more than 3 cups of coffee or 3 cups of tea per day. Too much caffeine (found in coffee and tea) can make the baby restless.
- Give 4-6 months exclusively breastfeeding because breast milk is the healthiest nutrition for the baby. After 4-6 months the baby should receive supplementary feeding because breastfeeding no longer covers the daily nutritional requirements of the growing baby.
- Do not lose more than 0.5 kg weight per week, otherwise your baby will get through breastfeeding too much toxins. Toxins in the human body are stored in fatty tissues.