High tea consumption reduces hip fracture risk among women
Objectives:
Several studies have been conducted on the relationship between tea intake and the risk of osteoporosis. The results from these studies are, however, inconsistent. Therefore, this review article (meta-analysis) has been conducted.
Does tea intake reduce risk of osteoporosis?
Study design:
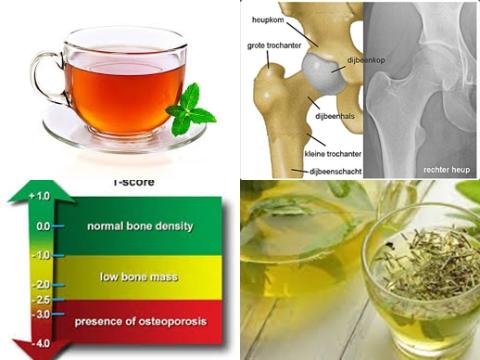
This review article included 2 prospective cohort studies, 4 cross-sectional studies and 11 case-control studies with 107,819 cases (people with osteoporosis). In the present study, the main symptom of osteoporosis was hip fracture.
10 studies - case-control and cohort studies were all of high quality - were in relative high quality (over 6 stars) with an average NOS score of 7.23.
The heterogeneity in the present review article mainly came from Asia group, female group, prospective cohort study group and case-control study group.
There was no publication bias of the meta-analysis about tea consumption and osteoporosis.
Results and conclusions:
The investigators found for the highest versus the lowest categories of tea consumption a significantly reduced risk of 38% [total OR = 0.62, 95% CI = 0.46-0.83, I2 = 94%, p 0 .01] for osteoporosis. However, when reducing heterogeneity, the overall OR [95% CI = 0.57-0.74, I2 = 30%] was still significant.
Subgroup analysis showed that tea consumption significantly reduced the risk of osteoporosis in all examined subgroups.
The investigators found stratified by categories of osteoporosis, a significantly reduced risk of 26% [OR = 0.74, 95% BI = 0.63-0.88] for hip fracture.
The investigators found among women a significantly reduced risk of 27% [OR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.54-0.99] for osteoporosis.
The investigators concluded that high tea consumption reduces risk of osteoporosis, particularly hip fracture and particularly among women. However, the exact mechanism of the relationship between tea consumption and osteoporosis still needs further research.
Original title:
Association between tea consumption and osteoporosis: A meta-analysis by Sun K, Wang L, [...], Li X.
Link:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5728912/
Additional information of El Mondo:
Find more information/studies on tea consumption and elderly right here.